How to Set Up a CI/CD Pipeline Using GitHub Actions (Step-by-Step Guide)
Managing a WordPress site can be frustrating when you have to manually upload themes or plugins for every minor change.
What if your code could automatically deploy to your WordPress site whenever you push updates to GitHub?
That’s where CI/CD with GitHub Actions makes life easier.
In this simple guide, you’ll learn how to set up a CI/CD pipeline that automatically updates your WordPress theme or plugin from GitHub to your web server.
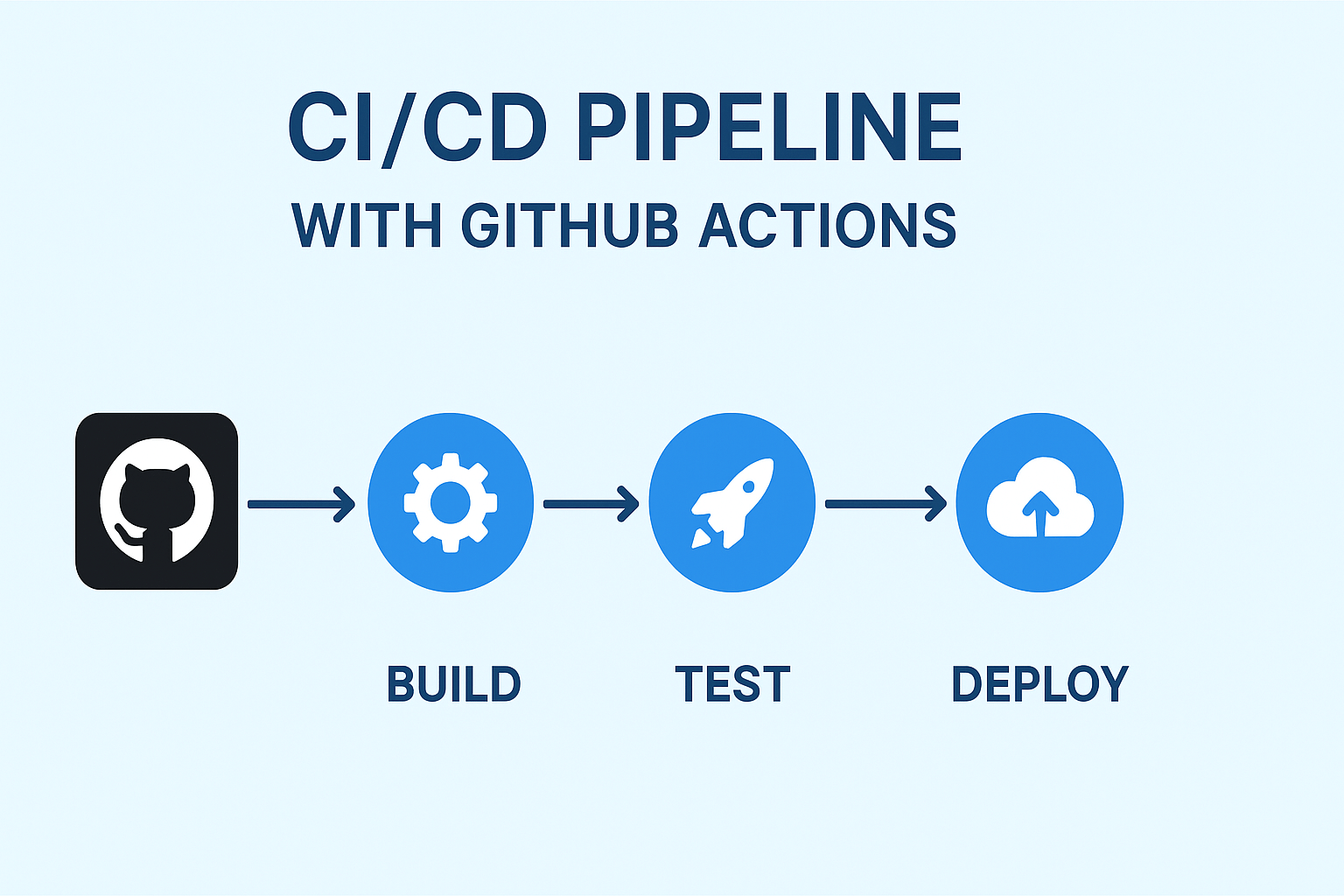
What Is CI/CD?
CI/CD stands for Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment.
- Continuous Integration (CI): Runs automated checks whenever you push code to GitHub — for example, linting or testing.
- Continuous Deployment (CD): Automatically deploys your changes to your website when everything looks good.
In short: You push code → GitHub checks it → GitHub uploads it to your server automatically.
What You’ll Need
Before setting up GitHub Actions, make sure you have:
A WordPress site hosted on a server (like DigitalOcean, AWS, or cPanel).
SSH access to that server (so GitHub can connect securely).
A GitHub repository containing your WordPress theme or plugin.
- A WordPress site hosted on a server (like DigitalOcean, AWS, or cPanel).
- SSH access to that server (so GitHub can connect securely).
- A GitHub repository containing your WordPress theme or plugin.
- Basic understanding of Git (push, pull, etc.).
Step 1: Prepare Your Repository
If you’re working on a theme, your folder structure might look like this:
theme-name/
┣━ functions.php
┣━ style.css
┣━ templates/
┗━ assets/
┗━ ....If it’s a plugin, it could look like:
plugin-name/
┣━ my-plugin.php
┣━ includes/
┗━ assets/
Push this folder to your GitHub repository.
Step 2: Create GitHub Action Workflow
Inside your GitHub repository, create a new file at:
.github/workflows/deploy.ymlNow paste this code:
name: Deploy WordPress Theme or Plugin
on:
push:
branches:
- main # deploy only when pushing to the main branch.
- branch-name You can add it on new line with - branch name
jobs:
deploy:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout code
uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Setup SSH
uses: webfactory/ssh-agent@v0.9.0
with:
ssh-private-key: ${{ secrets.SSH_KEY }}
- name: Deploy via rsync
run: |
rsync -avz --delete \
--exclude '.git*' \
./ ${{ secrets.SSH_USER }}@${{ secrets.SSH_HOST }}:/var/www/html/wp-content/themes/theme-name/
First, the workflow checks out your code from GitHub. Then it sets up an SSH connection using a private key from GitHub secrets, allowing secure access to your server. Finally, it uses rsync to upload your theme or plugin, updating files on the server and removing any old ones, while skipping Git-related files.
Step 3: Add GitHub Secrets
Go to your repository’s settings:
Settings → Secrets and variables → Actions → New repository secret
Add the following:
SSH_HOST | yourserver.com |
SSH_USER | ubuntu (or your SSH username) |
SSH_KEY | Paste your private SSH key here |
This keeps your credentials safe and hidden from your code.
Step 4: Test the Deployment
Now, whenever you make changes to your theme or plugin and push them to the main branch, GitHub Actions will automatically:
- Connect to your server via SSH
- Upload the latest files
- Replace the old version in your WordPress folder
You can view progress in the Actions tab on GitHub.
